Personal | One weekend in September 2025
API Development practice using Kaggle's Amazon Sales Data

OVERVIEW
Understanding APIs
After onboarding to Dwellci AI, I felt a strong need to understand API development, because every product's success boils down to the API layer. I wanted to start simple, practicing API endpoints and CRUD operations. I used Kaggle's Amazon Sales Data as my data source.
This page is essentially for me to record my learning process and reference for my future self, so I apologize if it's too long!
PLANNING
Visualizing the data flow
Figuring out the overall architecture and data flow was the first step. Then, the data structure and the API endpoints.
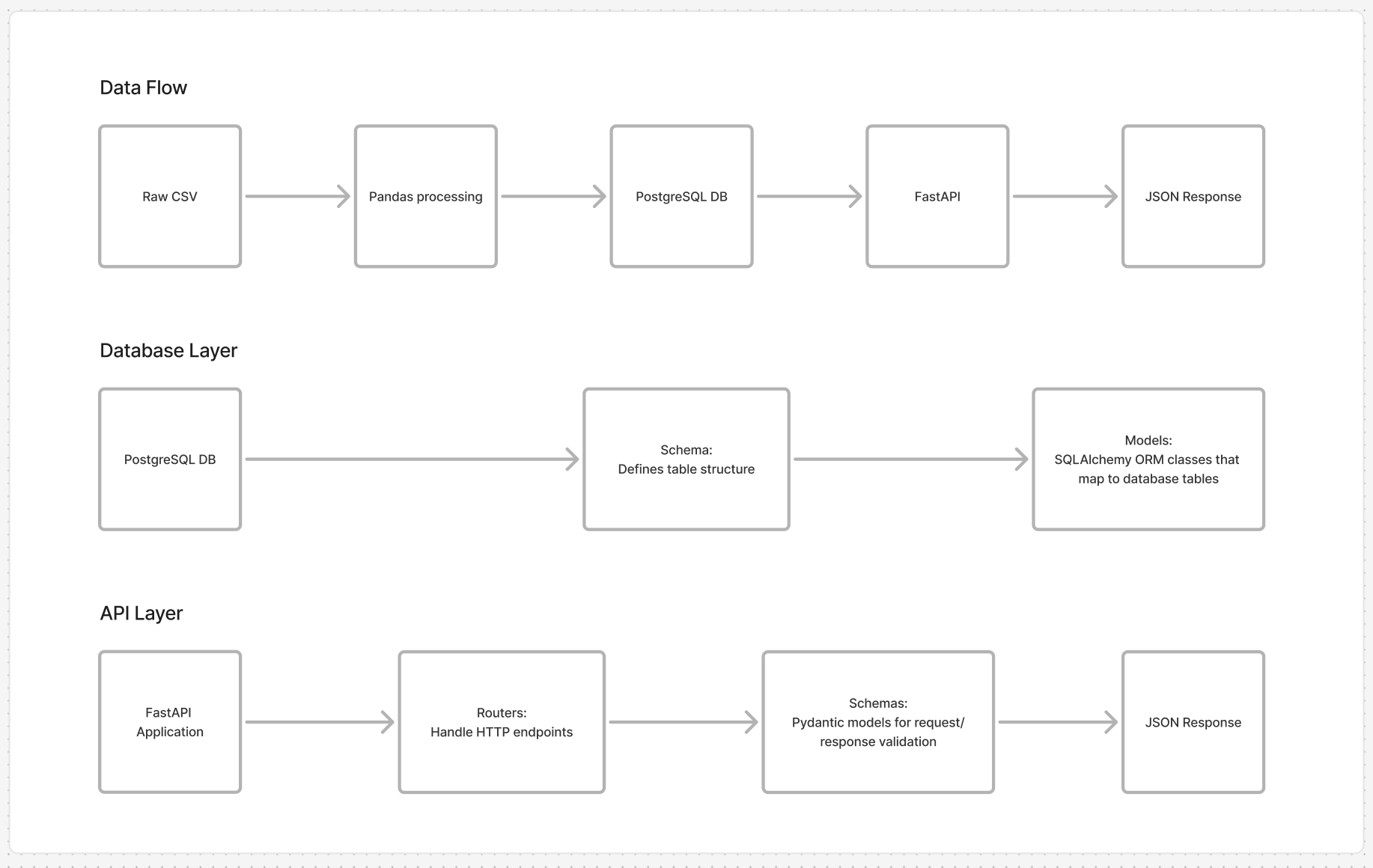
Core components
Schema(01_schema.sql)
Database initialization: creates the actual PostgreSQL tables. Runs during database setup, before any data processing.
CREATE TABLE public.products (
product_id TEXT PRIMARY KEY,
product_name TEXT NOT NULL,
category TEXT,
discounted_price TEXT,
actual_price TEXT NOT NULL,
discount_percentage TEXT,
rating TEXT,
rating_count TEXT,
about_product TEXT,
img_link TEXT,
product_link TEXT
);Models(models.py)
SQLAlchemy ORM layer: python classes that represent database tables. Runs when routers need to query/insert data, between database and API logic.
class Product(Base):
__tablename__ = "products"
product_id = Column(Text, primary_key = True)
product_name = Column(Text, nullable=True)
category = Column(Text)
discounted_price = Column(Text)
actual_price = Column(Text)
discount_percentage = Column(Text)
rating = Column(Text)
rating_count = Column(Text)
about_product = Column(Text)
img_link = Column(Text)
product_link = Column(Text)Routers(products.py)
FastAPI layer: handles HTTP requests and logic. Runs when API endpoints are called, between HTTP requests and database operations.
router = APIRouter(prefix="/products", tags=["products"])
@router.get("/{product_id}", response_model=schemas.ProductOut)
def get_product(
product_id: str,
db: Session = Depends(get_db)
):
prod = db.get(models.Product, product_id)
if not prod:
raise HTTPException(status_code=404, detail="Product not found")
return prodSchemas(schemas.py)
API validation layer: validates incoming data and formats outgoing data. Runs during request/response processing, between HTTP requests and database operations.
class ProductOut(BaseModel):
product_id: str
product_name: str
category: str
discounted_price: str
actual_price: str
discount_percentage: str
rating: str
rating_count: str
about_product: str
img_link: str
product_link: strCOMPLETE FLOW & ARCHITECTURE
Once the core components were defined, I was able to put together the complete flow and architecture.
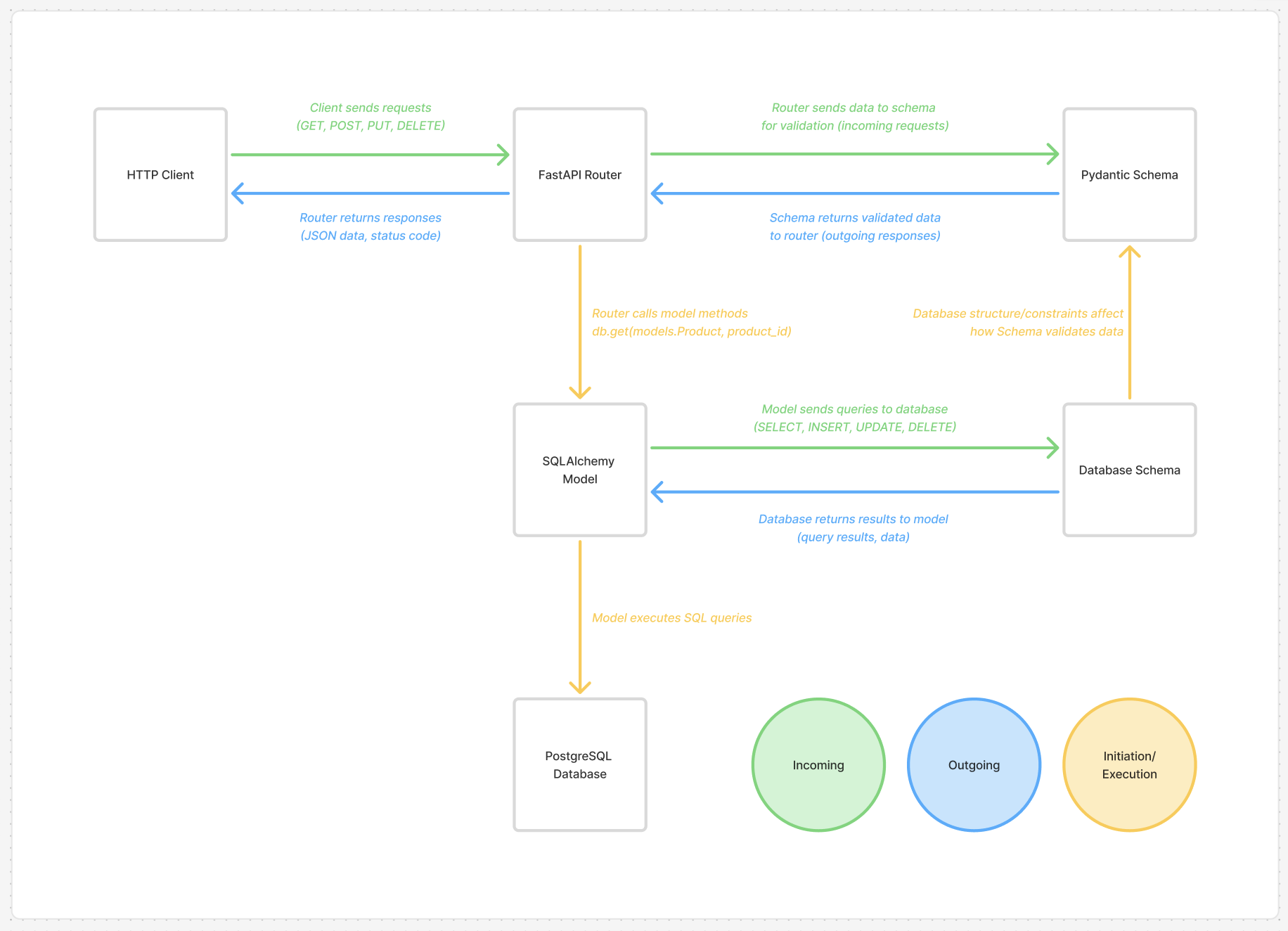
API ENDPOINTS
HTTP methods & CRUD operations
HTTP and CRUD are very similar, but there are some differences. HTTP methods are technical protocols, determining how data is transferred over the internet. CRUD are database operations, determining what you do with the data.

GET & READ
Reads data from database -- no side effects, only returns data
SELECT * FROM products WHERE product_id = ?
@router.get("/{product_id}", response_model=schemas.ProductOut) --> # GET /products/{product_id}
def get_product( --> # Query parameter
product_id: str, --> # Path parameter, required
db: Session = Depends(get_db)
):
prod = db.get(models.Product, product_id) --> # READ
if not prod:
raise HTTPException(status_code=404, detail="Product not found")
return prodPOST & CREATE
Creates new data in database -- creates a new record
INSERT INTO products (product_id, product_name, category, ...) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ...)
@router.post("/", response_model=schemas.ProductOut) --> # POST /products/{product_id}
def create_product( --> # Query parameter
payload: schemas.ProductUpdate, --> # Request body, contains the field to update
db: Session = Depends(get_db)
):
prod = models.Product(**payload.model_dump()) --> # CREATE
db.add(prod)
db.commit()
return prodPUT & UPDATE
Updates existing data in database -- updates a record
UPDATE products SET product_name=?, category=?, ... WHERE product_id = ?
@router.put("/{product_id}", response_model=schemas.ProductOut) --> # PUT /products/{product_id}
def update_product( --> # Query parameter
product_id: str, --> # Path parameter
payload: schemas.ProductUpdate, --> # Request body, contains the field to update
db: Session = Depends(get_db)
):
prod = db.get(models.Product, product_id) --> # READ
if not prod:
raise HTTPException(status_code=404, detail="Product not found")
for field, value in payload.model_dump().items():
# prod = product object from DB
# field = name of attribute to update e.g., product_name, category
# value = new value for the attribute
setattr(prod, field, value) --> # UPDATE
db.commit()
db.refresh(prod)
return prodDELETE & DELETE
Deletes data from database -- deletes a record
DELETE FROM products WHERE product_id = ?
@router.delete("/{product_id}", response_model=schemas.ProductOut) --> # DELETE /products/{product_id}
def update_product( --> # Query parameter
product_id: str, --> # Path parameter
db: Session = Depends(get_db)
):
prod = db.get(models.Product, product_id) --> # READ
if not prod:
raise HTTPException(status_code=404, detail="Product not found")
db.delete(prod) --> # DELETE
db.commit()
return prodQUERY PARAMETERS
Query parameters & filtering
FastAPI Query()
Query() allows you to define query parameters in the URL. It's a dictionary of key-value pairs.
def get_products(
category: Optional[str] = Query(None, description="Category") --> # Optional query parameter
):SQLAlchemy .filter()
Filtering database queries based on parameters.
def get_products(
category: Optional[str] = Query(None, description="Category")
):
query = db.query(models.Product) --> # Query the database
if category:
query = query.filter(models.Product.category == category) --> # Filter if existsOptional vs Required
Understanding the difference between optional and required parameters.
def get_products(
category: Optional[str] = Query(None, description="Category") --> # Optional
):
query = db.query(models.Product)
def get_product(
product_id: str, --> # Required
):
prod = db.get(models.Product, product_id) --> # Specific productREQUEST & RESPONSE
Pydantic BaseModel
Pydantic is a library for data validation and parsing. BaseModel is a class that defines the structure of the data. It automatically validates the incoming data and converts its type appropriately. It also serializes python objects to JSON and provides helpful error messages.
Request schemas (ProductCreate, ProductUpdate)
Defining the structure for incoming data.
class ProductCreate(BaseModel): {
product_name: str = Field(None, description="...") "product_name": "Dyson Hair Dryer",
category: str = Field(None, description="...") "category": "Home",
discounted_price: str = Field(None, description="...") "discounted_price": "59.99",
... }Response schemas (ProductOut)
Defining the structure for outgoing data.
class ProductOut(BaseModel): {
product_id: str = Field(..., description="...") "product_id": "prod_123",
product_name: str = Field(None, description="...") "product_name": "Dyson Hair Dryer",
category: str = Field(None, description="...") "category": "Home",
discounted_price: str = Field(None, description="...") "discounted_price": "59.99",
actual_price: str = Field(None, description="...") "actual_price": "149.99",
... }ERROR HANDLING
Error handling & status codes
| Status Code | Description | When Used |
|---|---|---|
| 200 | OK | Successful GET request |
| 201 | Created | Successful POST request |
| 400 | Bad Request | Invalid request data |
| 404 | Not Found | Resource doesn't exist |
| 422 | Unprocessable Entity | Validation error |
| 500 | Internal Server Error | Server-side error |
| 503 | Service Unavailable | Service temporarily down |
| 504 | Gateway Timeout | Request timeout |
Quick Debugging Guide
| Error Type | Common Causes | Quick Fixes |
|---|---|---|
| Connection Error | Database not running, wrong connection string | Check Docker, verify DATABASE_URL |
| Validation Error | Missing required fields, wrong data types | Check request body, validate schemas |
| Import Error | Missing dependencies, wrong module paths | Run pip install, check PYTHONPATH |
| Authentication Error | Invalid API key, expired tokens | Regenerate keys, check token expiry |
| Database Error | Table doesn't exist, constraint violations | Run migrations, check foreign keys |
| Timeout Error | Slow queries, network issues | Add indexes, increase timeout limits |
| Memory Error | Large datasets, memory leaks | Use pagination, optimize queries |
| Configuration Error | Missing env vars, wrong settings | Check .env file, validate config |